⚙️Spring Boot 启动流程源码解析
文章目录
- ⚙️Spring Boot 启动流程源码解析
- 🎯 一、Spring Boot 启动流程概览
-
- 🔄 启动流程全景图
- ⏱️ 启动阶段时间线
- 🏗️ 二、SpringApplication 初始化阶段
-
- 🚀 SpringApplication.run() 入口分析
- 🔧 应用类型推断机制
- 📦 工厂加载机制
- ⚙️ 三、启动前准备:Banner、Environment、Listener
-
- 🚀 run() 方法执行流程
- 🎨 Banner 打印机制
- 🌍 Environment 准备过程
- 🔄 四、创建 ApplicationContext 与加载 BeanDefinition
-
- 🏗️ 应用上下文创建机制
- 📋 上下文准备阶段
- 🔧 上下文初始器应用
- ⚡ 五、refresh 阶段与自动装配结合点
-
- 🔄 refreshContext() 核心流程
- 🎯 Spring Boot 特有的刷新扩展
- 🔧 自动装配与刷新的集成点
- 📢 六、应用启动事件与回调机制
-
- 🎯 Spring Boot 启动事件体系
- 👂 事件监听器机制
- 🔄 运行监听器获取机制
- 💻 七、自定义监听器与启动钩子实践
-
- 🛠️ 自定义启动监听器
- 🔧 启动性能监控工具
- 🎯 自定义应用运行器
- 🔧 启动故障诊断工具
- 💎 八、总结:从 main() 到容器就绪的生命线
-
- 🎯 Spring Boot 启动流程核心总结
- 🔄 启动流程完整时序图
- 🚀 性能优化建议
- 🔧 调试与监控最佳实践
🎯 一、Spring Boot 启动流程概览
🔄 启动流程全景图
Spring Boot 应用启动时序图:
main() SpringApplication ApplicationContext BeanFactory EventListener run() 初始化SpringApplication 加载应用上下文初始器 加载应用事件监听器 阶段1: 启动前准备 打印Banner 准备Environment 发布ApplicationStartingEvent 阶段2: 创建应用上下文 创建ApplicationContext实例 准备应用上下文 发布ApplicationContextInitializedEvent 阶段3: 刷新上下文 refresh() 加载Bean定义 实例化单例Bean 发布ContextRefreshedEvent 阶段4: 启动完成 发布ApplicationReadyEvent 返回ApplicationContext main() SpringApplication ApplicationContext BeanFactory EventListener
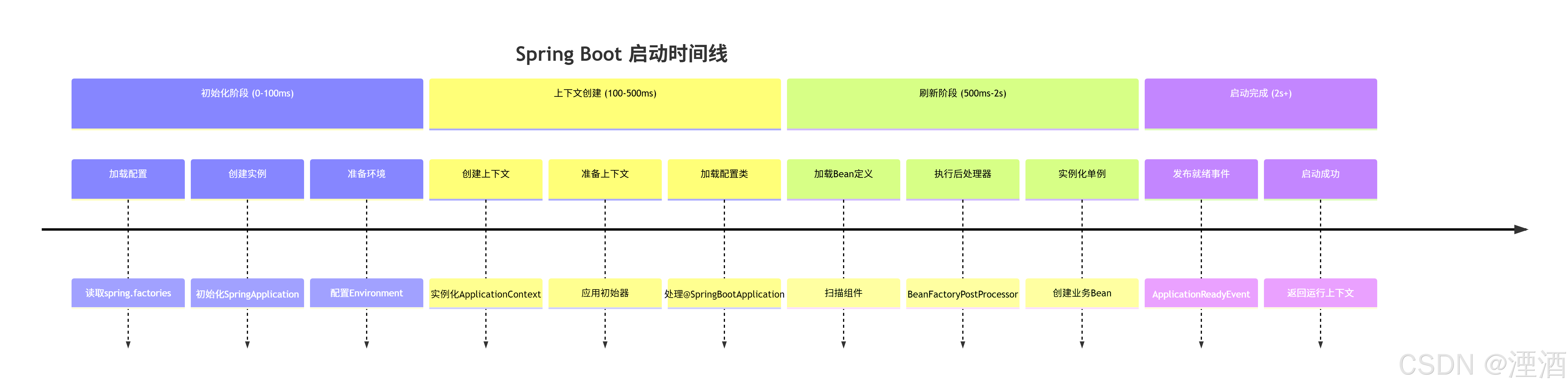
⏱️ 启动阶段时间线
关键启动节点时间分布:
🏗️ 二、SpringApplication 初始化阶段
🚀 SpringApplication.run() 入口分析
启动方法核心逻辑:
1public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) { 2 return run(new Class<?>[]{primarySource}, args); 3} 4 5public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) { 6 // 创建SpringApplication实例并执行run方法 7 return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args); 8} 9
SpringApplication 构造函数源码:
1public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { 2 this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; 3 4 // 1. 设置主配置类(不能为null) 5 Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); 6 this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); 7 8 // 2. 推断应用类型(Servlet、Reactive、None) 9 this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); 10 11 // 3. 加载应用上下文初始器(从spring.factories) 12 setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); 13 14 // 4. 加载应用事件监听器(从spring.factories) 15 setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); 16 17 // 5. 推断主应用类(从堆栈跟踪) 18 this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); 19} 20
🔧 应用类型推断机制
WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath() 源码:
1static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { 2 // 检查类路径是否存在特定的类来判断应用类型 3 4 if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) 5 && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) 6 && !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) { 7 return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; // WebFlux应用 8 } 9 10 for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) { 11 if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { 12 return WebApplicationType.NONE; // 非Web应用 13 } 14 } 15 16 return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; // Servlet Web应用 17} 18
应用类型推断的类路径检查:
1// 关键类路径检查常量 2private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet"; 3private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler"; 4private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer"; 5private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { 6 "javax.servlet.Servlet", 7 "org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" 8}; 9
📦 工厂加载机制
getSpringFactoriesInstances() 方法实现:
1private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) { 2 return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[]{}); 3} 4 5private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { 6 ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader(); 7 8 // 1. 使用SpringFactoriesLoader加载实现类名称 9 Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); 10 11 // 2. 创建实例 12 List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); 13 14 // 3. 排序(支持@Order注解) 15 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); 16 return instances; 17} 18
⚙️ 三、启动前准备:Banner、Environment、Listener
🚀 run() 方法执行流程
SpringApplication.run() 完整实现:
1public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { 2 // 1. 创建启动计时器 3 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); 4 stopWatch.start(); 5 6 // 2. 初始化上下文和异常报告器 7 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; 8 Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); 9 10 // 3. 设置Headless模式 11 configureHeadlessProperty(); 12 13 try { 14 // 4. 获取运行监听器并发布启动事件 15 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); 16 listeners.starting(); 17 18 try { 19 // 5. 准备环境 20 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); 21 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); 22 23 // 6. 打印Banner 24 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); 25 26 // 7. 创建应用上下文 27 context = createApplicationContext(); 28 29 // 8. 准备异常报告器 30 exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, 31 new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); 32 33 // 9. 准备应用上下文 34 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); 35 36 // 10. 刷新上下文(核心阶段) 37 refreshContext(context); 38 39 // 11. 刷新后处理(空实现,子类可扩展) 40 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); 41 42 // 12. 停止计时器 43 stopWatch.stop(); 44 45 // 13. 发布启动完成事件 46 if (this.logStartupInfo) { 47 new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); 48 } 49 listeners.started(context); 50 51 // 14. 执行Runner回调 52 callRunners(context, applicationArguments); 53 54 } catch (Throwable ex) { 55 // 异常处理 56 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); 57 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 58 } 59 60 // 15. 发布应用就绪事件 61 listeners.ready(context); 62 return context; 63 64 } catch (Throwable ex) { 65 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); 66 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 67 } 68} 69
🎨 Banner 打印机制
Banner 打印实现细节:
1private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { 2 // 1. 检查是否禁用Banner 3 if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) { 4 return null; 5 } 6 7 // 2. 获取Banner资源 8 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = (this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader 9 : new DefaultResourceLoader(getClassLoader()); 10 11 // 3. 使用BannerPrinter打印 12 SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(resourceLoader, this.banner); 13 14 // 4. 根据模式选择输出流 15 if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) { 16 return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger); 17 } 18 return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out); 19} 20
自定义 Banner 实现示例:
1@Component 2public class CustomBanner implements Banner { 3 4 private static final String[] BANNER = { 5 " ___ ___ _ _ ", 6 " | \\/ | | | | | ", 7 " | . . | ___ __| |___| |__ ", 8 " | |\\/| |/ _ \\/ _` / __| '_ \\ ", 9 " | | | | __/ (_| \\__ \\ | | |", 10 " \\_| |_/\\___|\\__,_|___/_| |_|", 11 " " 12 }; 13 14 @Override 15 public void printBanner(Environment environment, Class<?> sourceClass, PrintStream printStream) { 16 for (String line : BANNER) { 17 printStream.println(line); 18 } 19 20 String version = getVersion(); 21 printStream.println(" :: Spring Boot :: " + version); 22 printStream.println(); 23 } 24 25 private String getVersion() { 26 try { 27 return SpringBootVersion.getVersion(); 28 } catch (Exception ex) { 29 return "v2.7.0"; 30 } 31 } 32} 33
🌍 Environment 准备过程
prepareEnvironment() 方法详解:
1private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, 2 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) { 3 4 // 1. 创建或获取Environment 5 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment(); 6 7 // 2. 配置Environment(处理命令行参数等) 8 configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs()); 9 10 // 3. 发布Environment准备事件 11 listeners.environmentPrepared(environment); 12 13 // 4. 绑定Environment到SpringApplication 14 bindToSpringApplication(environment); 15 16 // 5. 检查是否自定义Environment 17 if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) { 18 environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, 19 deduceEnvironmentClass()); 20 } 21 22 // 6. 配置PropertySources 23 ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); 24 return environment; 25} 26
Environment 创建逻辑:
1private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() { 2 // 根据应用类型创建相应的Environment 3 if (this.environment != null) { 4 return this.environment; 5 } 6 7 switch (this.webApplicationType) { 8 case SERVLET: 9 return new StandardServletEnvironment(); 10 case REACTIVE: 11 return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment(); 12 default: 13 return new StandardEnvironment(); 14 } 15} 16
🔄 四、创建 ApplicationContext 与加载 BeanDefinition
🏗️ 应用上下文创建机制
createApplicationContext() 方法实现:
1protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { 2 // 1. 根据应用类型推断上下文类 3 Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; 4 if (contextClass == null) { 5 try { 6 switch (this.webApplicationType) { 7 case SERVLET: 8 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); 9 break; 10 case REACTIVE: 11 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); 12 break; 13 default: 14 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); 15 } 16 } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 17 throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + 18 "please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); 19 } 20 } 21 22 // 2. 使用反射创建实例 23 return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); 24} 25
默认上下文类配置:
1// 默认上下文类常量 2public static final String DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext"; 3public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebApplicationContext"; 4public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebApplicationContext"; 5
📋 上下文准备阶段
prepareContext() 方法深度解析:
1private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, 2 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { 3 4 // 1. 设置环境 5 context.setEnvironment(environment); 6 7 // 2. 后处理上下文(设置资源加载器、转换服务等) 8 postProcessApplicationContext(context); 9 10 // 3. 应用上下文初始器 11 applyInitializers(context); 12 13 // 4. 发布上下文准备事件 14 listeners.contextPrepared(context); 15 16 // 5. 打印启动信息 17 if (this.logStartupInfo) { 18 logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); 19 logStartupProfileInfo(context); 20 } 21 22 // 6. 注册特定的单例Bean 23 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); 24 beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); 25 if (printedBanner != null) { 26 beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); 27 } 28 29 // 7. 设置允许Bean定义覆盖 30 if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) { 31 beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); 32 } 33 34 // 8. 添加Bean后处理器(懒加载等) 35 if (this.lazyInitialization) { 36 context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor()); 37 } 38 39 // 9. 加载源(主配置类) 40 Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); 41 Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); 42 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); 43 44 // 10. 发布上下文加载事件 45 listeners.contextLoaded(context); 46} 47
🔧 上下文初始器应用
applyInitializers() 方法实现:
1protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 2 // 1. 遍历所有ApplicationContextInitializer 3 for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) { 4 Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(), 5 ApplicationContextInitializer.class); 6 7 // 2. 检查类型匹配 8 if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(context)) { 9 throw new IllegalStateException("Initializer " + initializer.getClass().getName() + 10 " requires context of type " + requiredType.getName() + ", but got " + context.getClass().getName()); 11 } 12 13 // 3. 应用初始器 14 initializer.initialize(context); 15 } 16} 17
典型的 ApplicationContextInitializer 示例:
1// Spring Boot 内置的初始器示例 2public class MyContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> { 3 4 @Override 5 public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { 6 // 1. 设置配置文件位置 7 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment(); 8 environment.addActiveProfile("dev"); 9 10 // 2. 添加自定义属性源 11 MapPropertySource customPropertySource = new MapPropertySource("custom", 12 Collections.singletonMap("app.custom.property", "value")); 13 environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(customPropertySource); 14 15 // 3. 注册自定义Bean 16 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) applicationContext.getBeanFactory(); 17 registry.registerBeanDefinition("customBean", 18 BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(CustomBean.class).getBeanDefinition()); 19 } 20} 21
⚡ 五、refresh 阶段与自动装配结合点
🔄 refreshContext() 核心流程
刷新上下文的关键调用:
1private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 2 // 1. 注册关闭钩子 3 if (this.registerShutdownHook) { 4 try { 5 context.registerShutdownHook(); 6 } catch (AccessControlException ex) { 7 // 在安全管理器环境中可能不允许 8 } 9 } 10 11 // 2. 执行刷新(委托给AbstractApplicationContext) 12 refresh(context); 13} 14 15protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { 16 // 委托给ApplicationContext的refresh方法 17 if (applicationContext instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { 18 ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh(); 19 } 20} 21
🎯 Spring Boot 特有的刷新扩展
SpringApplicationRefreshListener 的作用:
1// Spring Boot 对标准refresh的扩展 2@Component 3public class SpringBootRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> { 4 5 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringBootRefreshListener.class); 6 7 @Override 8 public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { 9 ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext(); 10 11 // 1. 记录刷新完成 12 logger.info("Application context refreshed: {}", context.getDisplayName()); 13 14 // 2. 执行启动后检查 15 performPostRefreshChecks(context); 16 17 // 3. 发布自定义事件 18 context.publishEvent(new ApplicationRefreshedEvent(context)); 19 } 20 21 private void performPostRefreshChecks(ApplicationContext context) { 22 // 检查关键Bean是否就绪 23 checkRequiredBeans(context); 24 25 // 验证配置属性 26 validateConfigurationProperties(context); 27 } 28} 29
🔧 自动装配与刷新的集成点
自动配置在刷新阶段的触发时机:
1// 在refresh()方法中的关键调用点 2@Override 3public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 4 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 5 // ... 标准refresh流程 6 7 // 关键点:调用BeanFactory后处理器(包括自动配置) 8 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 9 10 // ... 其他步骤 11 } 12} 13
自动配置的触发流程:
ApplicationContext BeanFactoryPostProcessor AutoConfigurationImportSelector SpringFactoriesLoader invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() selectImports() loadFactoryNames() 加载spring.factories 返回自动配置类列表 返回需要导入的配置类 注册自动配置Bean定义 ApplicationContext BeanFactoryPostProcessor AutoConfigurationImportSelector SpringFactoriesLoader
📢 六、应用启动事件与回调机制
🎯 Spring Boot 启动事件体系
完整的启动事件序列:
1public class SpringBootEventSequence { 2 3 /** 4 * 完整的启动事件发布顺序 5 */ 6 public void demonstrateEventSequence() { 7 // 1. ApplicationStartingEvent - 启动最开始 8 // 2. ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent - 环境准备完成 9 // 3. ApplicationContextInitializedEvent - 上下文初始化 10 // 4. ApplicationPreparedEvent - 上下文准备完成 11 // 5. ContextRefreshedEvent - 上下文刷新完成(Spring标准事件) 12 // 6. ApplicationStartedEvent - 应用启动完成 13 // 7. ApplicationReadyEvent - 应用准备就绪(可以接收请求) 14 // 8. AvailabilityChangeEvent - 应用状态变更 15 } 16} 17
👂 事件监听器机制
SpringApplicationRunListeners 的实现:
1class SpringApplicationRunListeners { 2 3 private final Log log; 4 private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners; 5 6 // 启动事件发布方法 7 void starting() { 8 for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : listeners) { 9 listener.starting(); 10 } 11 } 12 13 void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { 14 for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : listeners) { 15 listener.environmentPrepared(environment); 16 } 17 } 18 19 void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 20 for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : listeners) { 21 listener.contextPrepared(context); 22 } 23 } 24 25 void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 26 for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : listeners) { 27 listener.contextLoaded(context); 28 } 29 } 30 31 void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 32 for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : listeners) { 33 listener.started(context); 34 } 35 } 36 37 void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 38 for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : listeners) { 39 listener.ready(context); 40 } 41 } 42} 43
🔄 运行监听器获取机制
getRunListeners() 方法实现:
1private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) { 2 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class }; 3 4 // 1. 从spring.factories加载SpringApplicationRunListener实现 5 List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners = getSpringFactoriesInstances( 6 SpringApplicationRunListener.class, parameterTypes, this, args); 7 8 // 2. 创建运行监听器包装器 9 return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, listeners); 10} 11
典型的 SpringApplicationRunListener:
1public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered { 2 3 private final SpringApplication application; 4 private final String[] args; 5 private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster; 6 7 public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) { 8 this.application = application; 9 this.args = args; 10 this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); 11 12 // 注册应用监听器 13 for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) { 14 this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); 15 } 16 } 17 18 @Override 19 public void starting() { 20 // 发布ApplicationStartingEvent 21 this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args)); 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { 26 // 发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 27 this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent( 28 this.application, this.args, environment)); 29 } 30 31 // 其他事件发布方法... 32} 33
💻 七、自定义监听器与启动钩子实践
🛠️ 自定义启动监听器
完整的启动事件监听器示例:
1@Component 2@Slf4j 3public class ComprehensiveStartupListener implements 4 ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>, Ordered { 5 6 private long startupStartTime; 7 private Map<String, Long> phaseTimestamps = new LinkedHashMap<>(); 8 9 @PostConstruct 10 public void init() { 11 this.startupStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 12 log.info("🚀 应用启动监听器已初始化"); 13 } 14 15 @Override 16 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { 17 recordPhaseTimestamp(event.getClass().getSimpleName()); 18 19 // 处理各种启动事件 20 if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent) { 21 handleStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event); 22 } else if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) { 23 handleEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event); 24 } else if (event instanceof ApplicationContextInitializedEvent) { 25 handleContextInitializedEvent((ApplicationContextInitializedEvent) event); 26 } else if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) { 27 handlePreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event); 28 } else if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) { 29 handleContextRefreshedEvent((ContextRefreshedEvent) event); 30 } else if (event instanceof ApplicationStartedEvent) { 31 handleStartedEvent((ApplicationStartedEvent) event); 32 } else if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent) { 33 handleReadyEvent((ApplicationReadyEvent) event); 34 } 35 } 36 37 private void handleStartingEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) { 38 log.info("📋 1. 应用启动开始"); 39 logApplicationInfo(event.getSpringApplication()); 40 } 41 42 private void handleEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) { 43 log.info("🌍 2. 环境准备完成"); 44 logEnvironmentInfo(event.getEnvironment()); 45 } 46 47 private void handleContextInitializedEvent(ApplicationContextInitializedEvent event) { 48 log.info("🏗️ 3. 应用上下文初始化完成"); 49 } 50 51 private void handlePreparedEvent(ApplicationPreparedEvent event) { 52 log.info("📦 4. 应用准备完成,Bean定义已加载"); 53 logBeanDefinitionCount(event.getApplicationContext()); 54 } 55 56 private void handleContextRefreshedEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { 57 log.info("🔄 5. 应用上下文刷新完成"); 58 logBeanStatistics(event.getApplicationContext()); 59 } 60 61 private void handleStartedEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) { 62 log.info("✅ 6. 应用启动完成"); 63 } 64 65 private void handleReadyEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent event) { 66 log.info("🎯 7. 应用准备就绪,可以处理请求"); 67 generateStartupReport(); 68 } 69 70 private void recordPhaseTimestamp(String phaseName) { 71 phaseTimestamps.put(phaseName, System.currentTimeMillis() - startupStartTime); 72 } 73 74 private void generateStartupReport() { 75 log.info("=== Spring Boot 启动性能报告 ==="); 76 phaseTimestamps.forEach((phase, timestamp) -> { 77 log.info(" {}: {}ms", phase, timestamp); 78 }); 79 80 long totalTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startupStartTime; 81 log.info(" 总启动时间: {}ms", totalTime); 82 log.info("=== 报告生成完成 ==="); 83 } 84 85 @Override 86 public int getOrder() { 87 return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE; // 最高优先级,最先执行 88 } 89} 90
🔧 启动性能监控工具
启动时间分析工具类:
1@Component 2@Slf4j 3public class StartupPerformanceMonitor { 4 5 private final Map<String, BeanInitInfo> beanInitInfo = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); 6 private long contextRefreshStartTime; 7 8 @EventListener 9 public void onContextRefreshed(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { 10 this.contextRefreshStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 11 log.info("开始监控Bean初始化性能..."); 12 } 13 14 @EventListener 15 public void onApplicationReady(ApplicationReadyEvent event) { 16 long totalTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - contextRefreshStartTime; 17 generatePerformanceReport(totalTime); 18 } 19 20 @Bean 21 public static BeanPostProcessor startupMonitorBeanPostProcessor() { 22 return new BeanPostProcessor() { 23 @Override 24 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { 25 // 记录Bean初始化开始时间 26 BeanInitInfo info = new BeanInitInfo(); 27 info.setStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); 28 info.setBeanName(beanName); 29 info.setBeanType(bean.getClass().getName()); 30 return bean; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { 35 // 记录Bean初始化完成时间 36 BeanInitInfo info = getBeanInitInfo(beanName); 37 if (info != null) { 38 info.setEndTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); 39 info.setDuration(info.getEndTime() - info.getStartTime()); 40 41 // 记录慢速Bean 42 if (info.getDuration() > 100) { // 超过100ms 43 log.warn("🐌 慢速Bean初始化: {} ({}ms)", beanName, info.getDuration()); 44 } 45 } 46 return bean; 47 } 48 }; 49 } 50 51 private void generatePerformanceReport(long totalTime) { 52 log.info("=== Bean初始化性能报告 ==="); 53 54 // 按初始化时间排序 55 beanInitInfo.values().stream() 56 .sorted(Comparator.comparingLong(BeanInitInfo::getDuration).reversed()) 57 .limit(10) // 显示最慢的10个Bean 58 .forEach(info -> { 59 String speed = info.getDuration() > 100 ? "🐌" : "⚡"; 60 log.info(" {} {}: {}ms", speed, info.getBeanName(), info.getDuration()); 61 }); 62 63 log.info("Bean初始化总时间: {}ms", totalTime); 64 log.info("监控的Bean数量: {}", beanInitInfo.size()); 65 } 66 67 @Data 68 private static class BeanInitInfo { 69 private String beanName; 70 private String beanType; 71 private long startTime; 72 private long endTime; 73 private long duration; 74 } 75} 76
🎯 自定义应用运行器
CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner 示例:
1@Component 2@Slf4j 3public class StartupRunner implements CommandLineRunner, ApplicationRunner, Ordered { 4 5 private final ApplicationContext context; 6 7 public StartupRunner(ApplicationContext context) { 8 this.context = context; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { 13 log.info("🔧 ApplicationRunner执行开始"); 14 performApplicationStartupTasks(); 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public void run(String... args) throws Exception { 19 log.info("🔧 CommandLineRunner执行开始"); 20 performCommandLineTasks(args); 21 } 22 23 private void performApplicationStartupTasks() { 24 // 1. 检查关键Bean是否就绪 25 checkCriticalBeans(); 26 27 // 2. 验证配置属性 28 validateConfiguration(); 29 30 // 3. 初始化应用数据 31 initializeApplicationData(); 32 33 log.info("✅ 应用启动任务完成"); 34 } 35 36 private void performCommandLineTasks(String[] args) { 37 if (args.length > 0) { 38 log.info("命令行参数: {}", Arrays.toString(args)); 39 40 // 处理特定的命令行参数 41 if (Arrays.asList(args).contains("--init-db")) { 42 initializeDatabase(); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 47 private void checkCriticalBeans() { 48 String[] criticalBeans = { 49 "dataSource", "entityManagerFactory", "transactionManager" 50 }; 51 52 for (String beanName : criticalBeans) { 53 if (context.containsBean(beanName)) { 54 log.info("✅ 关键Bean已就绪: {}", beanName); 55 } else { 56 log.warn("⚠️ 缺少关键Bean: {}", beanName); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 @Override 62 public int getOrder() { 63 return 1; // 执行顺序 64 } 65} 66
🔧 启动故障诊断工具
启动问题诊断器:
1@Component 2@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "app.startup.diagnostic", havingValue = "true") 3@Slf4j 4public class StartupDiagnosticTool { 5 6 @Autowired 7 private ApplicationContext context; 8 9 @EventListener 10 public void diagnoseOnReady(ApplicationReadyEvent event) { 11 log.info("=== 启动故障诊断开始 ==="); 12 13 // 1. 检查Bean定义冲突 14 checkBeanDefinitionConflicts(); 15 16 // 2. 检查循环依赖 17 checkCircularDependencies(); 18 19 // 3. 检查配置属性 20 checkConfigurationProperties(); 21 22 // 4. 检查数据库连接 23 checkDatabaseConnection(); 24 25 log.info("=== 启动故障诊断完成 ==="); 26 } 27 28 private void checkBeanDefinitionConflicts() { 29 try { 30 if (context instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) { 31 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = 32 ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).getBeanFactory(); 33 34 // 检查重复的Bean定义 35 String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames(); 36 Map<String, List<String>> typeToBeanNames = new HashMap<>(); 37 38 for (String beanName : beanNames) { 39 BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName); 40 String className = bd.getBeanClassName(); 41 if (className != null) { 42 typeToBeanNames.computeIfAbsent(className, k -> new ArrayList<>()) 43 .add(beanName); 44 } 45 } 46 47 // 报告冲突 48 typeToBeanNames.entrySet().stream() 49 .filter(entry -> entry.getValue().size() > 1) 50 .forEach(entry -> log.warn("🔴 Bean定义冲突: {} -> {}", 51 entry.getKey(), entry.getValue())); 52 } 53 } catch (Exception e) { 54 log.warn("Bean定义冲突检查失败: {}", e.getMessage()); 55 } 56 } 57 58 // 其他检查方法... 59} 60
💎 八、总结:从 main() 到容器就绪的生命线
🎯 Spring Boot 启动流程核心总结
启动阶段关键节点回顾:
| 阶段 | 关键方法 | 主要工作 | 发布事件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 初始化阶段 | SpringApplication 构造函数 | 推断 Web 应用类型(Servlet、Reactive)、加载 ApplicationContextInitializer 与 ApplicationListener | — |
| 环境准备阶段 | prepareEnvironment() | 构建 ConfigurableEnvironment,加载配置文件与系统属性,合并命令行参数 | ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent |
| 创建上下文阶段 | createApplicationContext() | 实例化具体类型的 ApplicationContext(如 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext) | ApplicationContextInitializedEvent |
| 上下文准备阶段 | prepareContext() | 应用 ApplicationContextInitializer,注册核心单例 Bean(如 springApplicationArguments) | ApplicationPreparedEvent |
| 上下文刷新阶段 | refreshContext() | 加载 Bean 定义、创建单例 Bean、初始化容器生命周期 | ContextRefreshedEvent |
| 启动完成阶段 | afterRefresh() | 执行 ApplicationRunner 与 CommandLineRunner,发布应用就绪事件 | ApplicationReadyEvent |
🔄 启动流程完整时序图
Spring Boot 应用启动完整流程:
User main() SpringApplication EventListener ApplicationContext BeanFactory Runner 执行java -jar SpringApplication.run() 阶段1: 初始化 推断应用类型 加载Initializer/Listener ApplicationStartingEvent 阶段2: 环境准备 创建Environment 处理配置属性 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 阶段3: 上下文创建 创建ApplicationContext 应用Initializer ApplicationContextInitializedEvent 阶段4: 上下文准备 准备上下文 注册单例Bean ApplicationPreparedEvent 阶段5: 刷新上下文 refresh() 加载Bean定义 实例化单例 ContextRefreshedEvent 阶段6: 启动完成 执行Runner ApplicationStartedEvent ApplicationReadyEvent 返回ApplicationContext 应用启动成功 User main() SpringApplication EventListener ApplicationContext BeanFactory Runner
🚀 性能优化建议
启动性能优化策略:
1@SpringBootApplication 2public class OptimizedApplication { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(OptimizedApplication.class); 6 7 // 1. 配置优化选项 8 app.setLazyInitialization(true); // 启用懒加载 9 app.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.CONSOLE); // 控制Banner输出 10 11 // 2. 排除不必要的自动配置 12 app.setDefaultProperties(Collections.singletonMap( 13 "spring.autoconfigure.exclude", 14 "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration" 15 )); 16 17 app.run(args); 18 } 19 20 @Configuration 21 @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "app.optimization.enabled", havingValue = "true") 22 public static class OptimizationConfig { 23 24 @Bean 25 public StartupOptimizer startupOptimizer() { 26 return new StartupOptimizer(); 27 } 28 } 29} 30
🔧 调试与监控最佳实践
生产环境启动监控配置:
1# application-prod.properties 2# 启动性能监控 3management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info,metrics,startup 4management.endpoint.startup.enabled=true 5 6# 详细的启动日志 7logging.level.org.springframework.boot=INFO 8logging.level.com.example=DEBUG 9 10# 启动超时设置 11spring.boot.startup.timeout=300s 12 13# 懒加载配置 14spring.main.lazy-initialization=true 15 16# 排除不必要的自动配置 17spring.autoconfigure.exclude=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration 18
《Spring Boot 启动流程源码解析》 是转载文章,点击查看原文。


