基础知识:
1.SDF 有符号距离场,且通过正负可以判断在物体外部还是内部,通常外正内负
这是RayMarching的灵魂支撑,能够通过一个数学函数,输入一个空间中的点,输出这个点到物体表面的最短距离(带符号)。可以使复杂的几何形状可以通过简单的 SDF运算来组合。比如,两个球体的 SDF 可以通过 min() 操作来融合,通过 max() 来相交,通过 abs()和减法来创造出“镂空”效果。
RayMarching 区别于正常的射线求交,根据他的中文翻译名,光线步进,可以比较生动的理解。
光并非直接打到物体表面求交然后渲染,而是每一步都计算和物体表面的SDF,从而安全前进,循环直道命中物体或者超出最大步数结束。
第一种制作方法:
球体采用XYZW四维向量,W表示球体半径
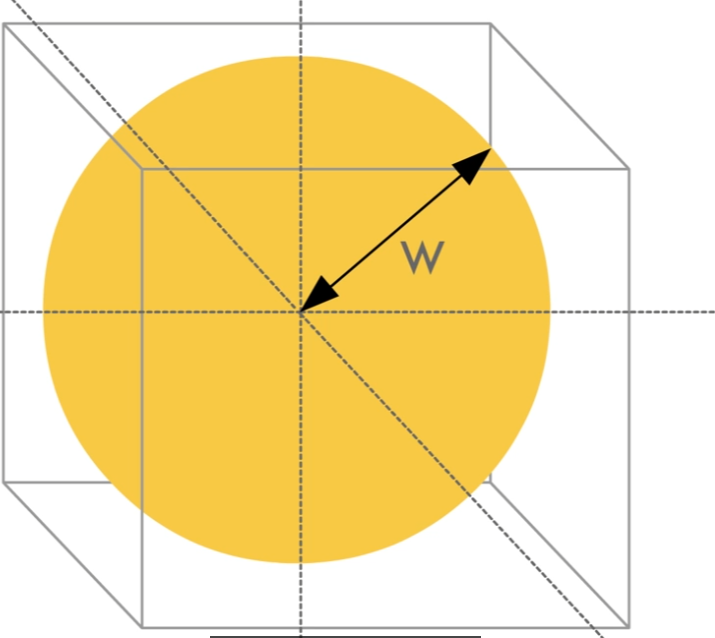
1// 版本1:简单的球体密度测试 2void raymarchv1_float( 3 float3 rayOrigin, // 光线起点 4 float3 rayDirection, // 光线方向 5 float numSteps, // 步进次数 6 float stepSize, // 步长 7 float densityScale, // 密度缩放 8 float4 Sphere, // 球体数据:xyz=中心位置, w=半径 9 out float result // 输出:累积密度 10) 11{ 12 float density = 0; 13 14 // 简单步进循环 15 for (int i = 0; i < numSteps; i++) 16 { 17 // 沿光线方向移动 18 rayOrigin += (rayDirection * stepSize); 19 20 // 计算到球心的距离 21 float sphereDist = distance(rayOrigin, Sphere.xyz); 22 23 // 如果点在球体内,增加密度 24 if (sphereDist < Sphere.w) 25 { 26 density += 0.1; // 固定密度值 27 } 28 } 29 30 // 应用密度缩放 31 result = density * densityScale; 32} 33
在此基础上能输出一个白色的圆环
光线步进-经典的三个参数:
numstep是步数,步数越大,光线越容易走出圆圈的范围,渲染出的效果越淡
stepSize是步长,步长越长,分层越明显, 越小,分层越不明显,越偏向全白
densityScale是密度缩放数值, result = density * densityScale;
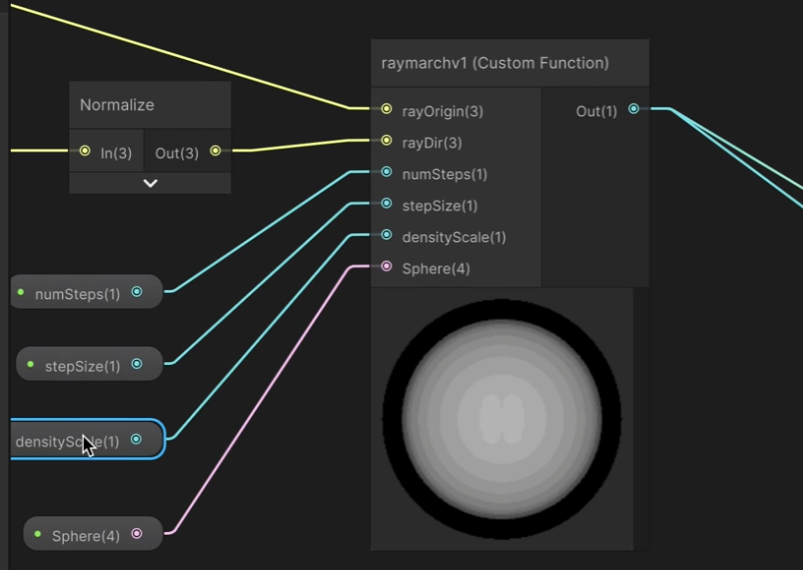

然后把球的节点更换增加一个3D体积纹理就可以变得更像云一些了
1// 版本2:使用3D纹理的基本实现 2void raymarchv2_float( 3 float3 rayOrigin, // 光线起点 4 float3 rayDirection, // 光线方向 5 float numSteps, // 步进次数 6 float stepSize, // 步长 7 float densityScale, // 密度缩放 8 UnityTexture3D volumeTex, // 3D体积纹理 9 UnitySamplerState volumeSampler, // 采样器 10 float3 offset, // 纹理偏移 11 out float result // 输出:累积密度 12) 13{ 14 float density = 0; 15 float transmission = 0; 16 17 // 基本步进循环 18 for (int i = 0; i < numSteps; i++) 19 { 20 // 沿光线方向移动 21 rayOrigin += (rayDirection * stepSize); 22 23 // 从3D纹理采样密度 24 float sampledDensity = SAMPLE_TEXTURE3D(volumeTex, volumeSampler, rayOrigin + offset).r; 25 26 // 累积密度 27 density += sampledDensity; 28 } 29 30 // 应用密度缩放 31 result = density * densityScale; 32} 33

参数还是同理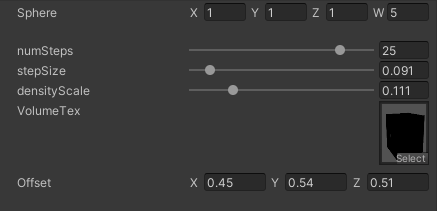
sphere四个参数控制圆心位置和半径
numsteps 确定步数,步长太少根本画不出圆,只有能走过圆的步长才能有形状,step数量确定有没有
step size 确定步长,步长越长数值越大
density scale 确定每一步的值的缩放尺寸
云越多,光线照射到物体上的光线方向数量就越少
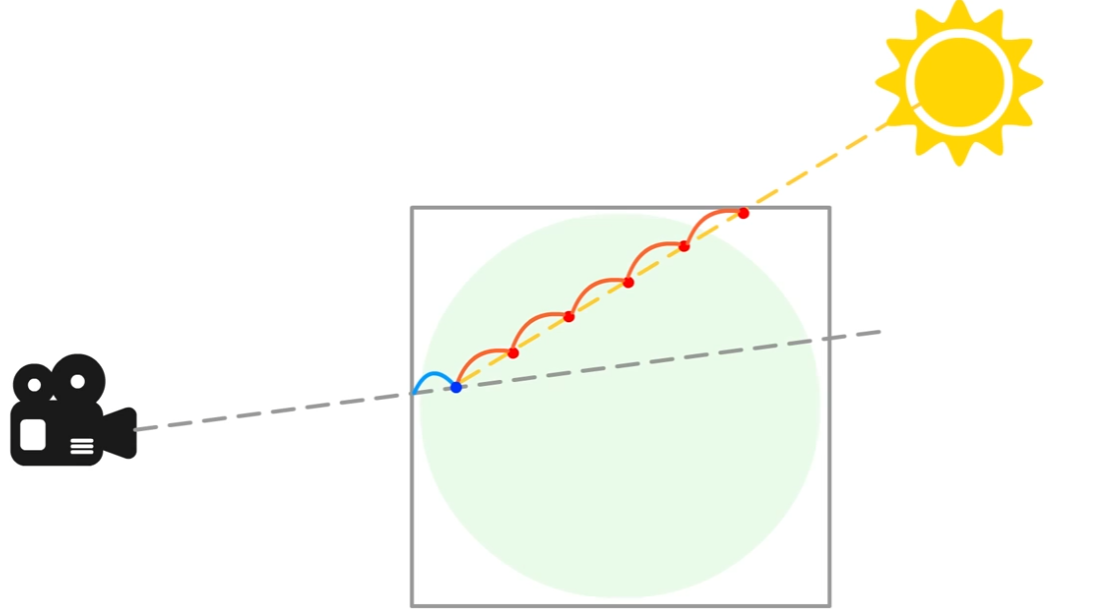
最终版本的代码如下
1void raymarch_float(float3 rayOrigin, float3 rayDirection, float numSteps, float stepSize, 2 float densityScale, UnityTexture3D volumeTex, UnitySamplerState volumeSampler, 3 float3 offset, float numLightSteps, float lightStepSize, float3 lightDir, 4 float lightAbsorb, float darknessThreshold, float transmittance, out float3 result) 5{ 6 float density = 0; 7 float transmission = 0; 8 float lightAccumulation = 0; 9 float finalLight = 0; 10 11 12 for (int i = 0; i < numSteps; i++) 13 { 14 rayOrigin += (rayDirection * stepSize); 15 16 //The blue dot position 17 float3 samplePos = rayOrigin + offset; 18 float sampledDensity = SAMPLE_TEXTURE3D(volumeTex, volumeSampler, samplePos).r; 19 density += sampledDensity * densityScale; 20 21 //light loop numLightSteps 数量直接影响性能 22 float3 lightRayOrigin = samplePos; 23 24 for (int j = 0; j < numLightSteps; j++) 25 { 26 //The red dot position 27 lightRayOrigin += -lightDir * lightStepSize; 28 float lightDensity = SAMPLE_TEXTURE3D(volumeTex, volumeSampler, lightRayOrigin).r; 29 //The accumulated density from samplePos to the light - the higher this value the less light reaches samplePos 30 lightAccumulation += lightDensity; 31 } 32 33 //The amount of light received along the ray from param rayOrigin in the direction rayDirection 34 float lightTransmission = exp(-lightAccumulation); 35 //shadow tends to the darkness threshold as lightAccumulation rises 36 float shadow = darknessThreshold + lightTransmission * (1.0 - darknessThreshold); 37 //The final light value is accumulated based on the current density, transmittance value and the calculated shadow value 38 finalLight += density * transmittance * shadow; 39 //Initially a param its value is updated at each step by lightAbsorb, this sets the light lost by scattering 40 transmittance *= exp(-density * lightAbsorb); 41 } 42 43 transmission = exp(-density); 44 45 result = float3(finalLight, transmission, transmittance); 46} 47
《[Unity Shader Base] RayMarching in Cloud Rendering》 是转载文章,点击查看原文。
