一.注解的定义与分类

注解的概念:
Java提供了一种原程序中的元素关联任何信息和任何元数据的途径和方法
JDK自带注解:
@Override 代表子类重写父类的方法
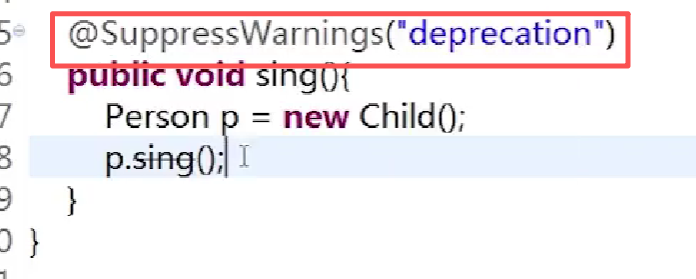
@Deprecated 代表该方法已经过时

@SuppressWarning 代表忽略警告Warnings
注解的分类:
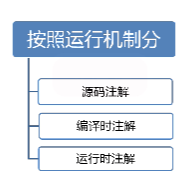
- 源码注解:注解只在源码中存在,编译成.class文件就不存在了
- 编译时注解:注解在源码和.class文件中都存在(@Override,@Deprecated这些都是)
- 运行时注解:在运行阶段还起作用,甚至会影响运行逻辑的注解(@Autowired)
注解的代价
凡事有得必有失,注解技术同样如此。使用注解也有一定的代价:
- 显然,它是一种侵入式编程,那么,自然就存在着增加程序耦合度的问题。
- 自定义注解的处理需要在运行时,通过反射技术来获取属性。如果注解所修饰的元素是类的非 public 成员,也可以通过反射获取。这就违背了面向对象的封装性。
- 注解所产生的问题,相对而言,更难以 debug 或定位。
二.自定义注解
1.自定义注解的语法要求
a.使用**@interface**关键字定义注解
b.成员以无参无异常方式声明
c.可以用default为成员指定一个默认值
d.其中成员类型是受限的,合法的类型包括原始类型及String,Class,Annotation,Enumeration
e.如果注解只有一个成员,则成员名必须为value(),在使用时可以忽略成员名和赋值号(=)
f.注解类可以没有成员,没有成员的注解称为标识注解(例如@Overrride)
1//以下成员都是不合法的,因为成员要无参数,无异常 2String desc(int a); 3String desc() throws Exception; 4 5//成员类型为受限的,以下不可以 6Map desc();
1//语法: 2//注解属性只能使用 public 或默认访问级别(即不指定访问级别修饰符)修饰。 3[访问级别修饰符] [数据类型] 名称() default 默认值; 4
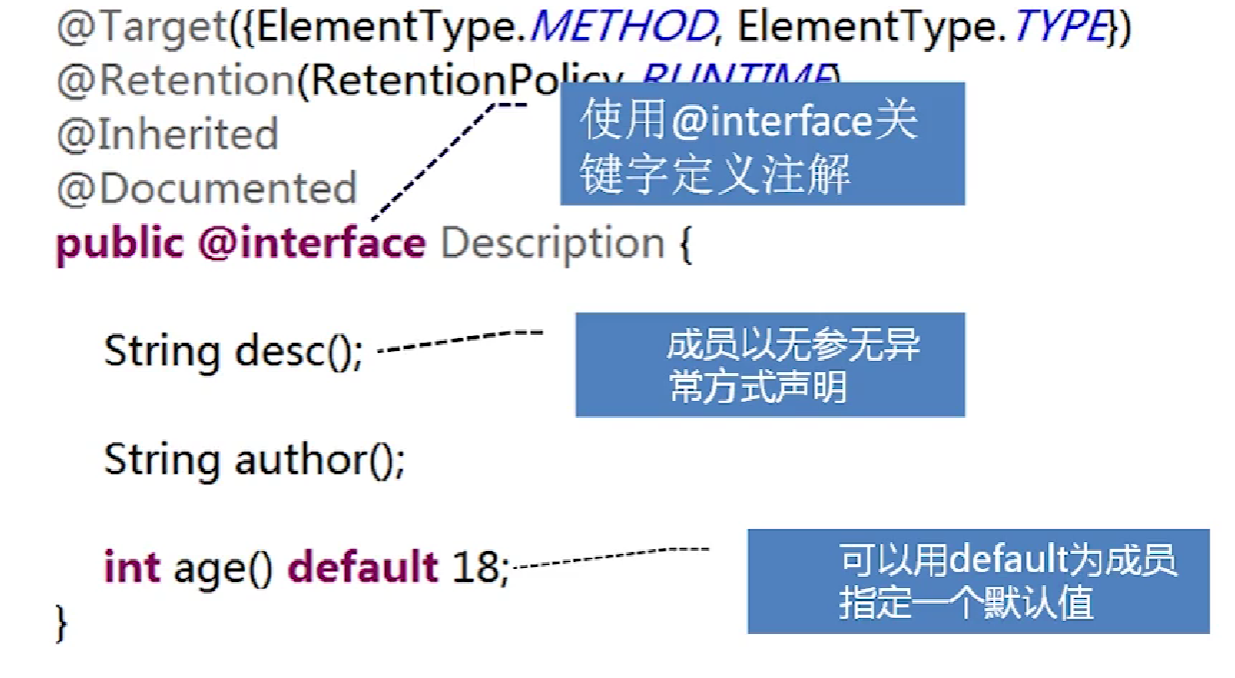
元注解:
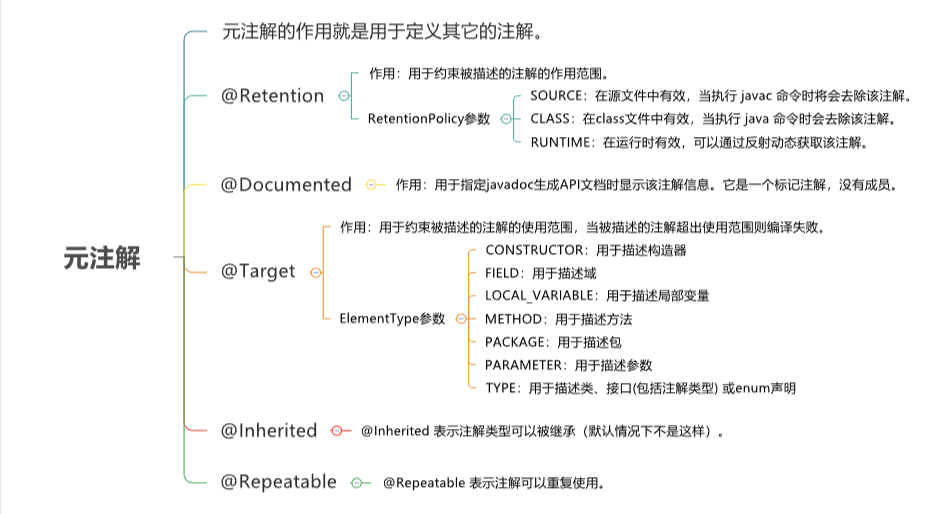
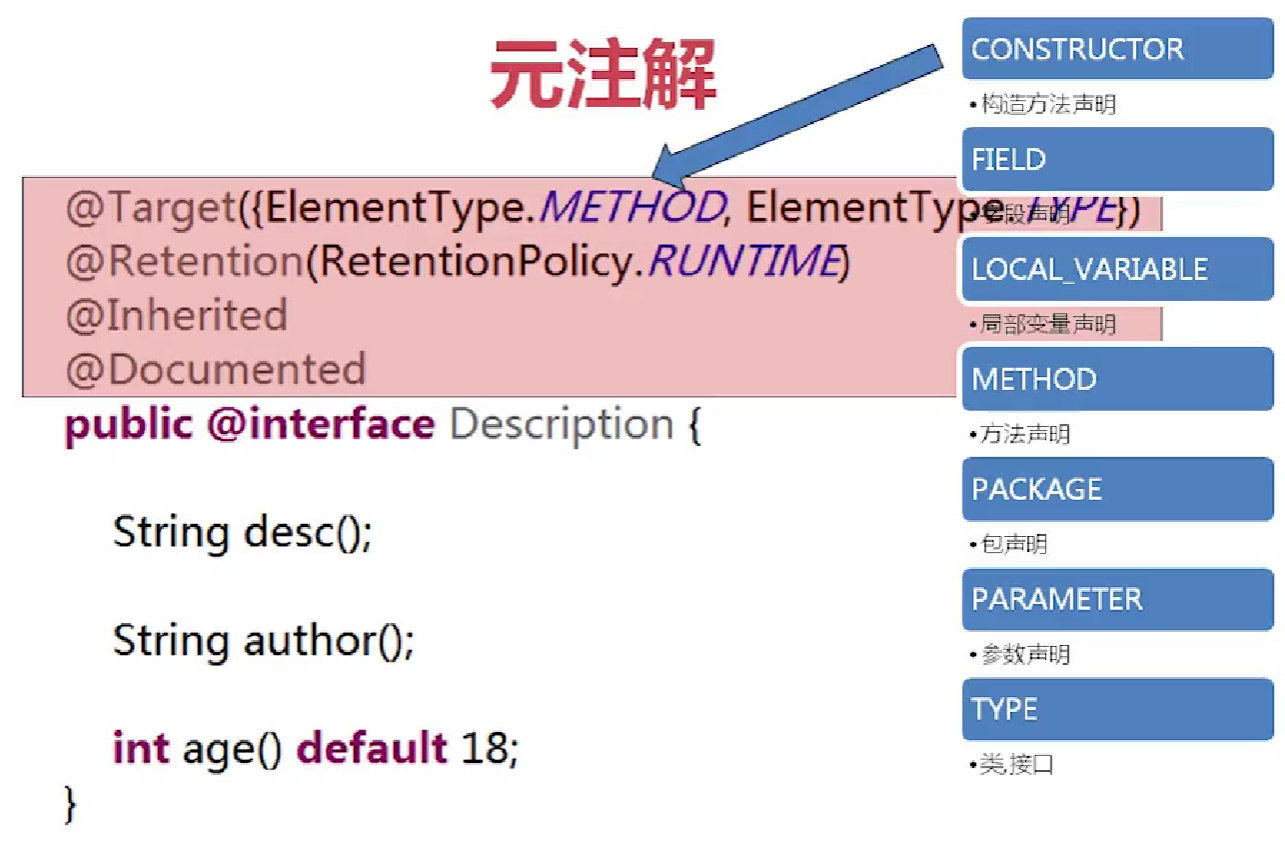
- @Target是作用域
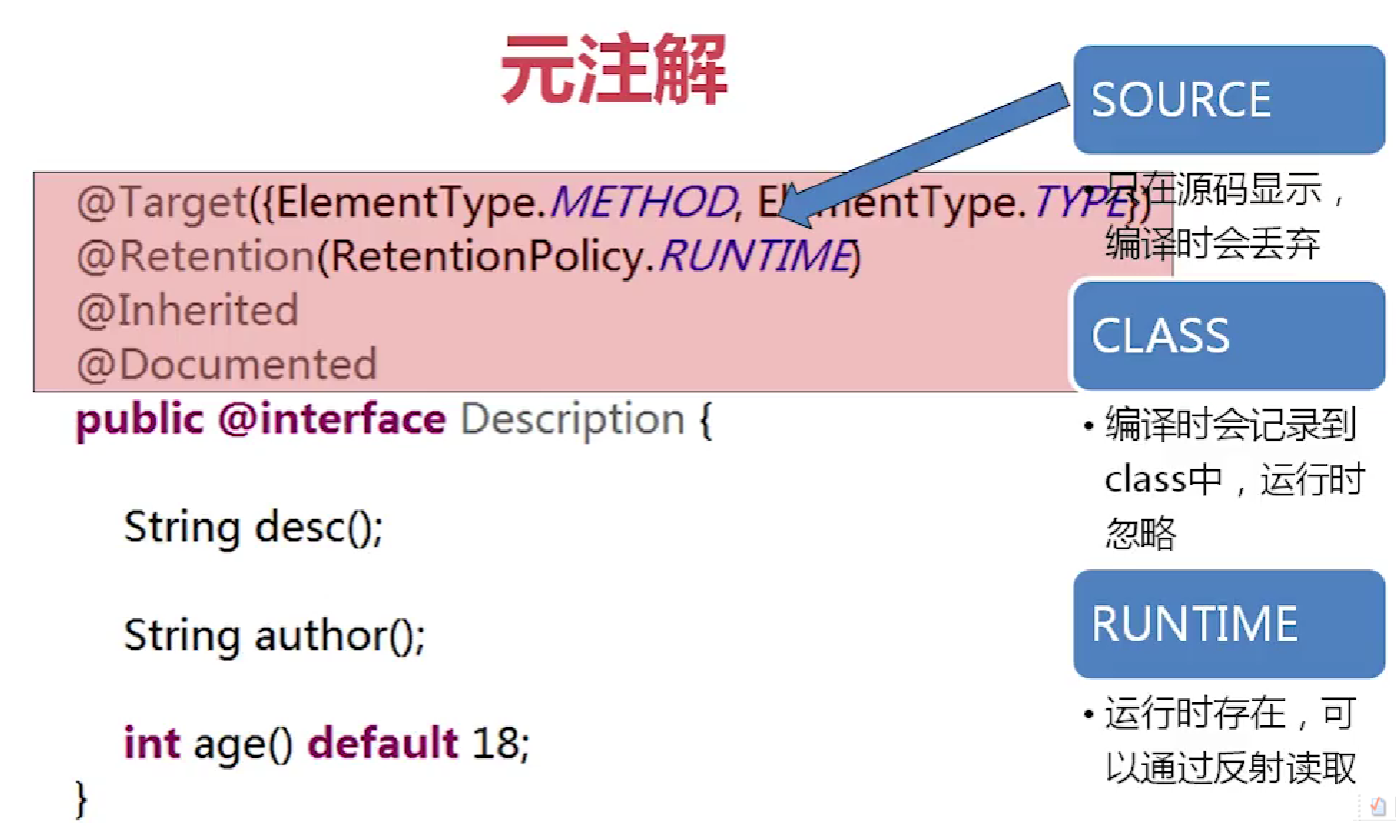
- @Retention生命周期
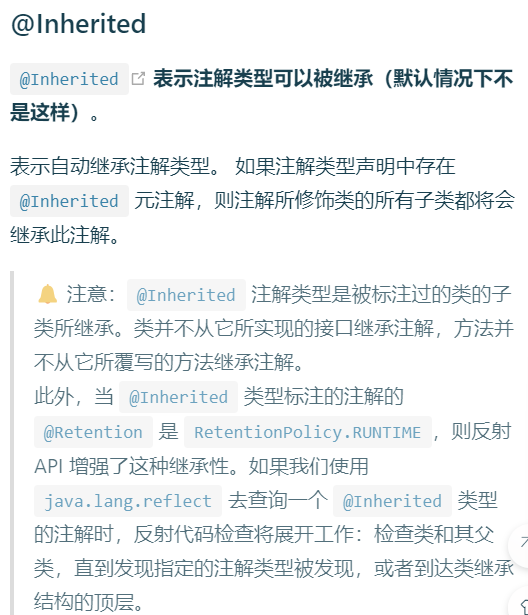
- @Inherited 这是一个标识型元注解,即允许继承(默认情况下不是这样)
- @Documented 生成javadoc时会包含注解
2.使用自定义注解

解析注解:
概念:通过反射获取类,函数或成员上的运行时注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑
1public static void main(String[] args){ 2 //1.使用类加载器加载类 3 try{ 4 Class c=Class.forName("com.ann.test.Child"); 5 //2.找到类上面的注解 6 boolean isExist=c.isAnnotation(Description.class); 7 if(isExist){ 8 //3.拿到注解实例 9 Description d=(Description)c.getAnnotation(Description.class); 10 System.out.println(d.value()); 11} 12 //4.找到方法上的注解 13 Method[] ms=c.getMethods(); 14 for(Method m:ms){ 15 boolean isExist=m.isAnnotation(Description.class); 16 if(isExist){ 17 Description d=(Description)m.getAnnotation(Description.class); 18 System.out.println(d.value())}} 19} 20 21}catch(ClassNotFoundException e){ 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23} 24}
三.注解实战
需求:
- 有一张用户表,字段包括用户ID,用户名,昵称,年纪,性别,所在城市,邮箱,手机号
- 方便的对每个字段或者字段的组合条件进行检索,并打印出SQL
1package reflectionandproxy.test; 2//1.首先考虑代码如何与数据库进行映射--->Filter和数据库字段相似 3@Table("user") 4public class Filter { 5 @Column("id") 6 private int id; 7 8 @Column("user_name") 9 private String userName; 10 11 @Column("nick_name") 12 private String nickName; 13 14 @Column("age") 15 private int age; 16 17 @Column("city") 18 private String city; 19 20 @Column("email") 21 private String email; 22 23 @Column("mobile") 24 private String mobile; 25 26 public String getMobile() { 27 return mobile; 28 } 29 30 public void setMobile(String mobile) { 31 this.mobile = mobile; 32 } 33 34 public int getId() { 35 return id; 36 } 37 38 public void setId(int id) { 39 this.id = id; 40 } 41 42 public String getUserName() { 43 return userName; 44 } 45 46 public void setUserName(String userName) { 47 this.userName = userName; 48 } 49 50 public String getNickName() { 51 return nickName; 52 } 53 54 public void setNickName(String nickName) { 55 this.nickName = nickName; 56 } 57 58 public int getAge() { 59 return age; 60 } 61 62 public void setAge(int age) { 63 this.age = age; 64 } 65 66 public String getCity() { 67 return city; 68 } 69 70 public void setCity(String city) { 71 this.city = city; 72 } 73 74 public String getEmail() { 75 return email; 76 } 77 78 public void setEmail(String email) { 79 this.email = email; 80 } 81} 82
1package reflectionandproxy.test; 2 3import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 4import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 5import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 6import java.lang.annotation.Target; 7 8@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) 9@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 10public @interface Column { 11 String value();//数据库字段名 12}
1package reflectionandproxy.test; 2 3import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 4import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 5import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 6import java.lang.annotation.Target; 7 8@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 9@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 10 11public @interface Table { 12 String value();//表名 13}
1package reflectionandproxy.test; 2 3import java.lang.reflect.Field; 4import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; 5import java.lang.reflect.Method; 6 7public class Test { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Filter f1=new Filter(); 10 f1.setId(10);//查询ID为10的用户 11 12 Filter f2=new Filter(); 13 f2.setUserName("Tom");//模糊查询用户名为Tom的用户 14 15 Filter f3=new Filter(); 16 f3.setEmail("[email protected],[email protected],[email protected]");//查询邮箱为其中任意一个 17 18 //查询sql语句 19 String sql1=query(f1); 20 String sql2=query(f2); 21 String sql3=query(f3); 22 23 //输出 24 System.out.println(sql1); 25 System.out.println(sql2); 26 System.out.println(sql3); 27 } 28 29 private static String query(Filter f1) { 30 //2.接下来我们就考虑如何实现query方法 31 StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); 32 //a.获取到class 33 Class clazz=f1.getClass(); 34 //b.获取到table的名字 35 boolean exists = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Table.class); 36 if(! exists){ 37 return null; 38 } 39 Table table= (Table) clazz.getAnnotation(Table.class); 40 String tableName=table.value(); 41 sb.append("select * from ").append(tableName).append(" where 1=1"); 42 43 //c.获取到所有的字段 44 Field[] fields=clazz.getDeclaredFields(); 45 for (Field field : fields){ 46 //4.处理每个字段对应的sql语句 47 //4.1 获取到字段名 48 boolean exists1 = field.isAnnotationPresent(Column.class); 49 if(! exists1){ 50 continue; 51 } 52 Column column=field.getAnnotation(Column.class); 53 String columnName=column.value(); 54 //4.2 获取字段值 55 String fieldName = field.getName(); 56 String getMethodName = "get" + fieldName.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+fieldName.substring(1); 57 Object fieldValue=null; 58 try { 59 Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(getMethodName); 60 fieldValue =getMethod.invoke(f1); 61 } catch (NoSuchMethodException | IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) { 62 throw new RuntimeException(e); 63 } 64 //4.3拼装sql语句 65 if(fieldValue==null||(fieldValue instanceof Integer && ((Integer) fieldValue).intValue()==0)){ 66 continue; 67 } 68 sb.append(" and ").append(columnName).append(" = ").append(fieldValue); 69 } 70 return sb.toString(); 71 72 } 73}
控制台输出:
《全面解析java注解》 是转载文章,点击查看原文。

