专栏网址:https://blog.csdn.net/polarisrisingwar/category%5F13089386.html
专栏文章目录:专栏《Python自动化办公的192个实例项目》目录
本篇是《Python自动化办公的192个实例项目》专栏内容,内容主要为使用Python将Word文档导出为PDF格式 & 从Word文档中提取数据(以处理简历为例)。
欢迎关注、评论、提问。
文章目录
- 1. 项目9:将Word文档导出为PDF文档
-
- 准备环境
- 复制即可运行的完整代码
- 核心功能代码
- 2. 项目10:如何用Python从Word中提取数据:以处理简历为例
-
- 准备环境
- 准备测试数据
- 复制即可运行的完整代码
- 核心功能代码
-
- python-docx包
- csv包
- os包
- re包(正则表达式)
- Python对象处理
-
- 字符串处理
* 容器对象处理
- 字符串处理
- python-docx包
1. 项目9:将Word文档导出为PDF文档
准备环境
Python版本需要为3.8-3.14(pywin32的要求)
通过pip下载pywin32:
1pip install pywin32 2
复制即可运行的完整代码
1import os 2from win32com import client as wc 3 4def convert_word_to_pdf(word_path: str) -> str: 5 """ 6 将单个Word文档(doc/docx)转换为PDF格式,并返回转换后的文件路径 7 8 Args: 9 word_path (str): Word文件路径 10 11 Returns: 12 str: 转换后的PDF文件路径 13 14 Raises: 15 FileNotFoundError: 如果文件不存在 16 ValueError: 如果文件不是Word格式或路径无效 17 Exception: 转换过程中的其他错误 18 """ 19 # 参数验证 20 if not word_path or not isinstance(word_path, str): 21 raise ValueError("文件路径不能为空且必须是字符串") 22 23 # 检查文件是否存在 24 if not os.path.exists(word_path): 25 raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件不存在: {word_path}") 26 27 # 检查文件扩展名 28 valid_extensions = ('.doc', '.docx') 29 if not word_path.lower().endswith(valid_extensions): 30 raise ValueError(f"文件不是Word格式(.doc/.docx): {word_path}") 31 32 # 检查文件是否被占用(临时文件) 33 if os.path.basename(word_path).startswith('~'): 34 raise ValueError(f"文件可能是临时文件: {word_path}") 35 36 # 检查文件大小(避免处理空文件或损坏文件) 37 file_size = os.path.getsize(word_path) 38 if file_size == 0: 39 raise ValueError(f"文件为空: {word_path}") 40 41 word = None 42 doc = None 43 44 try: 45 # 创建Word应用实例 46 word = wc.Dispatch("Word.Application") 47 word.Visible = False 48 49 # 打开文档 50 doc = word.Documents.Open(word_path) 51 52 # 生成新的PDF文件路径 53 base_path = os.path.splitext(word_path)[0] 54 new_path = base_path + ".pdf" 55 56 # 处理文件名冲突 57 count = 0 58 while os.path.exists(new_path): 59 count += 1 60 new_path = f"{base_path}({count}).pdf" 61 62 # 保存为PDF格式(17代表PDF格式) 63 doc.SaveAs(new_path, 17) 64 65 # 验证转换后的文件 66 if not os.path.exists(new_path): 67 raise Exception("转换后的PDF文件未创建成功") 68 69 # 检查转换后的文件大小 70 if os.path.getsize(new_path) == 0: 71 raise Exception("转换后的PDF文件为空") 72 73 return new_path 74 75 except Exception as e: 76 # 清理可能创建的部分文件 77 if 'new_path' in locals() and os.path.exists(new_path): 78 try: 79 os.remove(new_path) 80 except: 81 pass 82 raise e 83 84 finally: 85 # 确保资源被正确释放 86 try: 87 if doc: 88 doc.Close() 89 except: 90 pass 91 92 try: 93 if word: 94 word.Quit() 95 except: 96 pass 97 98 99def main(): 100 """主函数:转换单个文件并显示结果""" 101 # 直接在代码中设置要转换的文件路径 102 word_file_path = r"D:\word_files\example.docx" # 修改为您要转换的Word文件路径 103 104 try: 105 print(f"开始转换文件: {word_file_path}") 106 107 # 转换文件 108 pdf_path = convert_word_to_pdf(word_file_path) 109 110 # 输出成功信息 111 print("\n" + "="*50) 112 print("✓ 文件转换成功!") 113 print(f"原始文件: {word_file_path}") 114 print(f"转换后文件: {pdf_path}") 115 print(f"文件大小: {os.path.getsize(pdf_path)} 字节") 116 print("="*50) 117 118 except FileNotFoundError as e: 119 print(f"✗ 错误: {e}") 120 print("请检查文件路径是否正确") 121 except ValueError as e: 122 print(f"✗ 错误: {e}") 123 print("请确保文件是有效的Word文档(.doc/.docx)") 124 except Exception as e: 125 print(f"✗ 转换失败: {e}") 126 print("可能是Word应用问题或文件损坏") 127 128 129if __name__ == "__main__": 130 main() 131
将代码复制到你的Python编辑器中,并修改D:\word_files\example.docx为您需要转换的Word文件路径即可。转换后的PDF文件与Word文件同名(如果已经存在了同名PDF文件,将加上(count)后缀以避免冲突)
核心功能代码
Word文档导出为PDF的核心功能代码为:
1import os 2from win32com import client as wc 3 4word = wc.Dispatch("Word.Application") 5word.Visible = False 6 7doc = word.Documents.Open(word_path) 8doc.SaveAs(new_path, 17) 9doc.Close() 10 11word.Quit() 12
将word_path对应的Word文档转换为new_path对应的PDF文档。支持doc和docx格式的Word文档。
doc.SaveAs(file_name, file_format)中file_format这个参数表示另存为文档的格式,参考https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/office/vba/api/word.wdsaveformat:
- 17:
wdFormatPDF- PDF格式 - 0:
wdFormatDocument- Microsoft Office Word 97-2003文档格式(.doc) - 16:
wdFormatDocumentDefault- Word默认文档格式(.docx) - 7:
wdFormatPDF- PDF格式(与17相同) - 8:
wdFormatXPS- XPS格式
2. 项目10:如何用Python从Word中提取数据:以处理简历为例
这个简单案例的数据是随机生成的10个格式相同的简历:
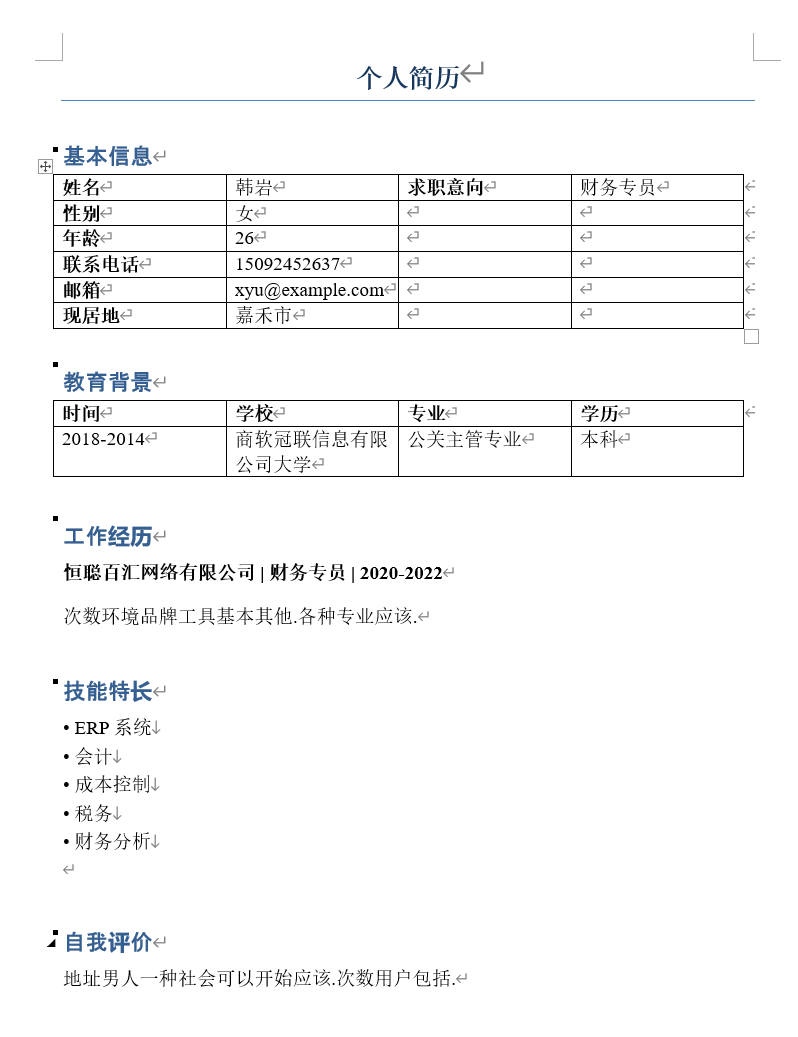
在实际工作中遇到的简历形式会更加多样化,需要根据实际情况来进行分析,甚至可能需要加入适当智能能力。我在此提供的只是一个简单样例,执行代码会解析目录下的所有Word格式简历:从表格中提取基本信息和教育背景,基本信息从表格中指定元素的位置获取,教育背景从表格中逐行获取;工作技能、技能特长、自我评价根据特定小标题和段落格式获取,都基本根据上图中这种格式来进行获取。最后的解析结果会保存到CSV文件中(CSV文件可以用Excel或WPS表格直接打开)。
如果读者在实际工作中遇到了更复杂的需求,也可以通过留言或私聊的方式咨询我获得答疑。
本案例生成测试数据的代码已经放在了下文中。由于是随机生成的,所以每次生成的数据都是不同的。如果您想要在本次案例中的数据,可以私聊我获取文件压缩包。
准备环境
通过pip下载python-docx:
1pip install python-docx 2
准备测试数据
通过pip下载faker:
1pip install faker 2
执行代码(简历文件会下载到工作路径下的resumes文件夹下):
(如果您需要执行这一部分代码的话,还需要注意的是,生成的Word文件默认使用中文宋体+英文Times New Roman格式,一般以中文为默认语言的Windows电脑中都已内置了这两种字体,如果您的电脑设置为其它语言需要注意)
1import os 2import random 3from docx import Document 4from docx.shared import Pt 5from docx.enum.text import WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH 6from docx.oxml.ns import qn 7 8from faker import Faker 9 10def set_document_font(doc): 11 """ 12 设置文档的默认字体为宋体和Times New Roman 13 """ 14 # 设置全局样式 15 style = doc.styles['Normal'] 16 font = style.font 17 font.name = 'Times New Roman' 18 font._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn('w:eastAsia'), u'宋体') 19 font.size = Pt(12) 20 21def set_paragraph_font(paragraph, bold=False, size=12): 22 """ 23 设置段落的字体 24 """ 25 for run in paragraph.runs: 26 run.font.name = 'Times New Roman' 27 run._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn('w:eastAsia'), u'宋体') 28 run.font.size = Pt(size) 29 run.font.bold = bold 30 31def generate_resume_docx(filename, resume_data): 32 """ 33 生成单个简历Word文档 34 35 Args: 36 filename (str): 保存的文件名 37 resume_data (dict): 简历数据 38 """ 39 doc = Document() 40 41 # 设置文档字体 42 set_document_font(doc) 43 44 # 添加标题 45 title = doc.add_heading('个人简历', 0) 46 title.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER 47 set_paragraph_font(title, bold=True, size=16) 48 49 # 添加个人信息表格 50 doc.add_heading('基本信息', level=1) 51 table = doc.add_table(rows=6, cols=4) 52 table.style = 'Table Grid' 53 54 # 填充基本信息表格 55 info_cells = [ 56 ("姓名", resume_data['name']), 57 ("性别", resume_data['gender']), 58 ("年龄", str(resume_data['age'])), 59 ("联系电话", resume_data['phone']), 60 ("邮箱", resume_data['email']), 61 ("现居地", resume_data['address']) 62 ] 63 64 for i, (label, value) in enumerate(info_cells): 65 table.cell(i, 0).text = label 66 table.cell(i, 1).text = value 67 table.cell(i, 2).text = "求职意向" if i == 0 else "" 68 table.cell(i, 3).text = resume_data['job_intention'] if i == 0 else "" 69 70 # 设置表格单元格字体 71 for j in range(4): 72 for paragraph in table.cell(i, j).paragraphs: 73 set_paragraph_font(paragraph, bold=(j == 0 or j == 2)) 74 75 # 教育背景 76 doc.add_heading('教育背景', level=1) 77 edu_table = doc.add_table(rows=2, cols=4) 78 edu_table.style = 'Table Grid' 79 80 # 表头 81 headers = ["时间", "学校", "专业", "学历"] 82 for i, header in enumerate(headers): 83 edu_table.cell(0, i).text = header 84 for paragraph in edu_table.cell(0, i).paragraphs: 85 set_paragraph_font(paragraph, bold=True) 86 87 # 教育信息 88 edu_table.cell(1, 0).text = resume_data['education']['period'] 89 edu_table.cell(1, 1).text = resume_data['education']['school'] 90 edu_table.cell(1, 2).text = resume_data['education']['major'] 91 edu_table.cell(1, 3).text = resume_data['education']['degree'] 92 93 # 设置教育信息行的字体 94 for i in range(4): 95 for paragraph in edu_table.cell(1, i).paragraphs: 96 set_paragraph_font(paragraph) 97 98 # 工作经历 99 doc.add_heading('工作经历', level=1) 100 for exp in resume_data['work_experience']: 101 p = doc.add_paragraph() 102 company_run = p.add_run(f"{exp['company']} | ") 103 company_run.bold = True 104 position_run = p.add_run(f"{exp['position']} | ") 105 position_run.bold = True 106 period_run = p.add_run(exp['period']) 107 period_run.bold = True 108 109 set_paragraph_font(p, bold=True) 110 111 desc_para = doc.add_paragraph(exp['description']) 112 set_paragraph_font(desc_para) 113 114 # 技能特长 115 doc.add_heading('技能特长', level=1) 116 skills_para = doc.add_paragraph() 117 for skill in resume_data['skills']: 118 skills_para.add_run(f"• {skill}\n") 119 set_paragraph_font(skills_para) 120 121 # 自我评价 122 doc.add_heading('自我评价', level=1) 123 self_eval_para = doc.add_paragraph(resume_data['self_evaluation']) 124 set_paragraph_font(self_eval_para) 125 126 # 保存文档 127 doc.save(filename) 128 print(f"已生成简历: {filename}") 129 130def generate_sample_resumes(num=10): 131 """ 132 生成指定数量的模拟简历 133 134 Args: 135 num (int): 简历数量,默认为10 136 """ 137 fake = Faker('zh_CN') 138 139 # 创建保存目录 - 使用os.path.join处理路径 140 resume_dir = os.path.join('resumes') 141 os.makedirs(resume_dir, exist_ok=True) 142 143 # 职位列表 144 jobs = ['软件工程师', '数据分析师', '产品经理', 'UI设计师', '市场营销', '人力资源', '财务专员', '运营专员'] 145 146 # 技能列表 147 skill_sets = { 148 '软件工程师': ['Python', 'Java', 'SQL', 'Linux', 'Git', 'Docker'], 149 '数据分析师': ['Python', 'SQL', 'Excel', 'Tableau', '统计学', '机器学习'], 150 '产品经理': ['Axure', 'Visio', '项目管理', '需求分析', '用户研究', 'PRD编写'], 151 'UI设计师': ['Photoshop', 'Sketch', 'Figma', 'Illustrator', '用户体验设计', '交互设计'], 152 '市场营销': ['市场分析', '营销策划', '社交媒体运营', '内容创作', '数据分析', '品牌管理'], 153 '人力资源': ['招聘', '培训', '绩效管理', '员工关系', 'HR系统', '劳动法'], 154 '财务专员': ['会计', '财务报表', '税务', '成本控制', '财务分析', 'ERP系统'], 155 '运营专员': ['内容运营', '用户运营', '活动策划', '数据分析', '社交媒体', 'SEO/SEM'] 156 } 157 158 # 生成简历 159 for i in range(num): 160 # 随机选择一个职位 161 job = random.choice(jobs) 162 163 # 生成简历数据 164 resume_data = { 165 'name': fake.name(), 166 'gender': random.choice(['男', '女']), 167 'age': random.randint(22, 35), 168 'phone': fake.phone_number(), 169 'email': fake.email(), 170 'address': fake.city(), 171 'job_intention': job, 172 'education': { 173 'period': f"{fake.year()}-{fake.year()}", 174 'school': fake.company() + "大学", 175 'major': fake.job() + "专业", 176 'degree': random.choice(['本科', '硕士', '博士']) 177 }, 178 'work_experience': [], 179 'skills': random.sample(skill_sets[job], random.randint(4, 6)), 180 'self_evaluation': fake.paragraph(nb_sentences=3) 181 } 182 183 # 生成工作经历 184 num_experiences = random.randint(1, 3) 185 for j in range(num_experiences): 186 start_year = 2020 - j * 2 187 resume_data['work_experience'].append({ 188 'company': fake.company(), 189 'position': job, 190 'period': f"{start_year}-{start_year+2}", 191 'description': fake.paragraph(nb_sentences=2) 192 }) 193 194 # 生成文档 - 使用os.path.join处理路径 195 safe_name = resume_data['name'].replace(' ', '_') 196 filename = os.path.join(resume_dir, f"简历_{safe_name}_{job}.docx") 197 generate_resume_docx(filename, resume_data) 198 199if __name__ == "__main__": 200 print("开始生成模拟简历...") 201 generate_sample_resumes(10) 202 print("简历生成完成!") 203
复制即可运行的完整代码
简历Word文档在resumes文件夹中,生成的resumes_data.csv就直接在工作路径下:
1import os 2import re 3import csv 4from docx import Document 5 6def extract_resume_info(filepath): 7 """ 8 从Word简历中提取信息 9 10 Args: 11 filepath (str): Word文档路径 12 13 Returns: 14 dict: 提取的简历信息 15 """ 16 try: 17 doc = Document(filepath) 18 resume_data = { 19 'filename': os.path.basename(filepath), 20 'name': '', 21 'gender': '', 22 'age': '', 23 'phone': '', 24 'email': '', 25 'address': '', 26 'job_intention': '', 27 'education_period': '', 28 'education_school': '', 29 'education_major': '', 30 'education_degree': '', 31 'work_experience': '', 32 'skills': '', 33 'self_evaluation': '' 34 } 35 36 # 提取基本信息 37 basic_info_extracted = False 38 education_extracted = False 39 in_work_experience = False 40 in_skills = False 41 in_self_evaluation = False 42 43 work_experiences = [] 44 skills_list = [] 45 46 for i, paragraph in enumerate(doc.paragraphs): 47 text = paragraph.text.strip() 48 49 # 跳过空段落 50 if not text: 51 continue 52 53 # 提取基本信息表格 54 if text == '基本信息' and not basic_info_extracted: 55 # 查找所有表格 56 for table in doc.tables: 57 # 检查表格是否包含基本信息 58 try: 59 if table.cell(0, 0).text == '姓名': 60 resume_data['name'] = table.cell(0, 1).text 61 resume_data['gender'] = table.cell(1, 1).text 62 resume_data['age'] = table.cell(2, 1).text 63 resume_data['phone'] = table.cell(3, 1).text 64 resume_data['email'] = table.cell(4, 1).text 65 resume_data['address'] = table.cell(5, 1).text 66 resume_data['job_intention'] = table.cell(0, 3).text 67 basic_info_extracted = True 68 break 69 except: 70 continue 71 72 if not basic_info_extracted: 73 # 如果没有找到表格,尝试从段落中提取 74 extract_basic_info_from_text(doc, resume_data) 75 basic_info_extracted = True 76 77 # 提取教育背景 78 elif text == '教育背景' and not education_extracted: 79 # 查找教育背景表格 80 for table in doc.tables: 81 try: 82 if table.cell(0, 0).text == '时间' and '学校' in table.cell(0, 1).text: 83 resume_data['education_period'] = table.cell(1, 0).text 84 resume_data['education_school'] = table.cell(1, 1).text 85 resume_data['education_major'] = table.cell(1, 2).text 86 resume_data['education_degree'] = table.cell(1, 3).text 87 education_extracted = True 88 break 89 except: 90 continue 91 92 # 提取工作经历 93 elif text == '工作经历': 94 in_work_experience = True 95 continue 96 elif in_work_experience and text and not text.startswith('技能特长') and not text.startswith('自我评价'): 97 # 检查是否是工作经历标题(包含公司、职位、时间,用 | 分隔) 98 if ' | ' in text: 99 parts = text.split(' | ') 100 if len(parts) >= 3: 101 # 提取公司、职位和时间 102 company = parts[0].strip() 103 position = parts[1].strip() 104 period = parts[2].strip() 105 106 work_experiences.append({ 107 'company': company, 108 'position': position, 109 'period': period 110 }) 111 # 否则,可能是工作描述,但我们主要关注标题信息 112 113 # 提取技能特长 114 elif text == '技能特长': 115 in_skills = True 116 in_work_experience = False 117 continue 118 elif in_skills and text and not text.startswith('自我评价'): 119 # 技能特长部分是以 • 开头的列表项 120 lines = text.split('\n') 121 for line in lines: 122 line = line.strip() 123 if line.startswith('•'): 124 skill = line[1:].strip() # 移除 • 符号 125 if skill: 126 skills_list.append(skill) 127 128 # 提取自我评价 129 elif text == '自我评价': 130 in_self_evaluation = True 131 in_skills = False 132 continue 133 elif in_self_evaluation and text: 134 resume_data['self_evaluation'] = text 135 in_self_evaluation = False 136 137 # 如果没有提取到基本信息,尝试其他方法 138 if not basic_info_extracted: 139 extract_basic_info_from_text(doc, resume_data) 140 141 # 将工作经历和技能列表转换为字符串 142 if work_experiences: 143 work_exp_str = " | ".join([ 144 f"{exp['company']} ({exp['position']}, {exp['period']})" 145 for exp in work_experiences 146 ]) 147 resume_data['work_experience'] = work_exp_str 148 149 if skills_list: 150 resume_data['skills'] = "; ".join(skills_list) 151 152 # 清理数据 153 clean_resume_data(resume_data) 154 155 return resume_data 156 157 except Exception as e: 158 print(f"提取简历信息时出错 {filepath}: {e}") 159 return None 160 161def extract_basic_info_from_text(doc, resume_data): 162 """ 163 从文档文本中提取基本信息 164 """ 165 for paragraph in doc.paragraphs: 166 text = paragraph.text 167 168 # 提取姓名 169 if not resume_data['name'] and len(text) <= 4 and not any(keyword in text for keyword in ['基本信息', '教育背景', '工作经历']): 170 resume_data['name'] = text 171 172 # 提取电话 173 phone_match = re.search(r'1[3-9]\d{9}', text) 174 if phone_match and not resume_data['phone']: 175 resume_data['phone'] = phone_match.group() 176 177 # 提取邮箱 178 email_match = re.search(r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b', text) 179 if email_match and not resume_data['email']: 180 resume_data['email'] = email_match.group() 181 182def clean_resume_data(resume_data): 183 """ 184 清理提取的简历数据 185 """ 186 # 清理年龄,只保留数字 187 if resume_data['age']: 188 age_match = re.search(r'\d+', resume_data['age']) 189 if age_match: 190 resume_data['age'] = age_match.group() 191 192def save_to_csv(resumes, csv_filename='resumes_data.csv'): 193 """ 194 将简历数据保存为CSV文件 195 196 Args: 197 resumes (list): 简历数据列表 198 csv_filename (str): CSV文件名 199 """ 200 if not resumes: 201 print("没有简历数据可保存") 202 return 203 204 # 定义CSV列名 205 fieldnames = [ 206 'filename', 'name', 'gender', 'age', 'phone', 'email', 'address', 207 'job_intention', 'education_period', 'education_school', 'education_major', 208 'education_degree', 'work_experience', 'skills', 'self_evaluation' 209 ] 210 211 with open(csv_filename, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8-sig') as csvfile: 212 writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames) 213 writer.writeheader() 214 215 for resume in resumes: 216 writer.writerow(resume) 217 218 print(f"简历数据已保存到: {csv_filename}") 219 220def analyze_resumes(directory='resumes'): 221 """ 222 分析目录中的所有简历 223 224 Args: 225 directory (str): 简历目录路径 226 """ 227 if not os.path.exists(directory): 228 print(f"目录不存在: {directory}") 229 return 230 231 resumes = [] 232 233 # 遍历目录中的所有Word文档 234 for filename in os.listdir(directory): 235 if filename.endswith('.docx'): 236 filepath = os.path.join(directory, filename) 237 print(f"正在处理: {filename}") 238 239 resume_data = extract_resume_info(filepath) 240 if resume_data: 241 resumes.append(resume_data) 242 243 # 输出分析结果 244 print("\n" + "="*50) 245 print("简历分析结果") 246 print("="*50) 247 248 # 统计基本信息 249 print(f"共处理简历: {len(resumes)} 份") 250 251 if not resumes: 252 return 253 254 # 按职位意向统计 255 job_counts = {} 256 for resume in resumes: 257 job = resume.get('job_intention', '未知') 258 job_counts[job] = job_counts.get(job, 0) + 1 259 260 print("\n职位意向分布:") 261 for job, count in job_counts.items(): 262 print(f" {job}: {count} 人") 263 264 # 平均年龄 265 ages = [] 266 for resume in resumes: 267 if resume['age'] and resume['age'].isdigit(): 268 ages.append(int(resume['age'])) 269 if ages: 270 avg_age = sum(ages) / len(ages) 271 print(f"\n平均年龄: {avg_age:.1f} 岁") 272 273 # 学历分布 274 degree_counts = {} 275 for resume in resumes: 276 degree = resume.get('education_degree', '未知') 277 degree_counts[degree] = degree_counts.get(degree, 0) + 1 278 279 print("\n学历分布:") 280 for degree, count in degree_counts.items(): 281 print(f" {degree}: {count} 人") 282 283 # 工作经历统计 284 work_exp_counts = {} 285 for resume in resumes: 286 work_exp = resume.get('work_experience', '') 287 if work_exp: 288 # 计算工作经历数量(通过 | 分隔符) 289 count = work_exp.count('|') + 1 290 work_exp_counts[count] = work_exp_counts.get(count, 0) + 1 291 292 print("\n工作经历数量分布:") 293 for count, freq in sorted(work_exp_counts.items()): 294 print(f" {count} 段经历: {freq} 人") 295 296 # 技能统计 297 skill_counts = {} 298 for resume in resumes: 299 skills_str = resume.get('skills', '') 300 if skills_str: 301 # 按分号分隔技能 302 skills = [skill.strip() for skill in skills_str.split(';') if skill.strip()] 303 for skill in skills: 304 skill_counts[skill] = skill_counts.get(skill, 0) + 1 305 306 # 取前10个最常用技能 307 top_skills = sorted(skill_counts.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:10] 308 print("\n最常用技能(前10):") 309 for skill, count in top_skills: 310 print(f" {skill}: {count} 次") 311 312 # 保存详细数据到CSV文件 313 save_to_csv(resumes, 'resumes_data.csv') 314 315 print(f"\n详细数据已保存到: resumes_data.csv") 316 317if __name__ == "__main__": 318 print("开始提取简历信息...") 319 analyze_resumes() 320 print("简历分析完成!") 321
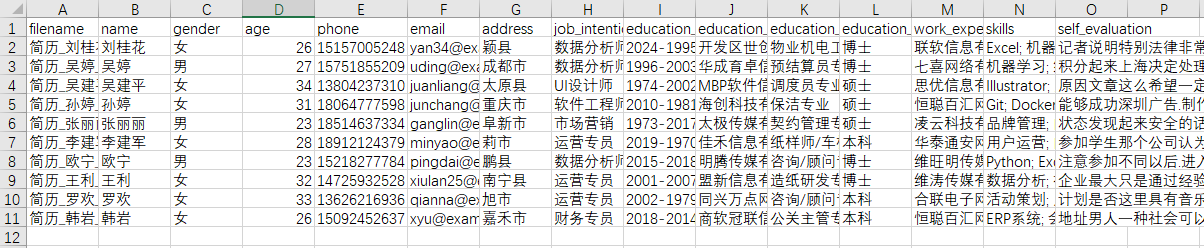
生成的resumes_data.csv为:
在生成过程中还会在终端输出:
1开始提取简历信息... 2正在处理: 简历_刘桂花_数据分析师.docx 3正在处理: 简历_吴婷_数据分析师.docx 4正在处理: 简历_吴建平_UI设计师.docx 5正在处理: 简历_孙婷_软件工程师.docx 6正在处理: 简历_张丽丽_市场营销.docx 7正在处理: 简历_李建军_运营专员.docx 8正在处理: 简历_欧宁_数据分析师.docx 9正在处理: 简历_王利_运营专员.docx 10正在处理: 简历_罗欢_运营专员.docx 11正在处理: 简历_韩岩_财务专员.docx 12 13================================================== 14简历分析结果 15================================================== 16共处理简历: 10 份 17 18职位意向分布: 19 数据分析师: 3 人 20 UI设计师: 1 人 21 软件工程师: 1 人 22 市场营销: 1 人 23 运营专员: 3 人 24 财务专员: 1 人 25 26平均年龄: 28.3 岁 27 28学历分布: 29 博士: 4 人 30 硕士: 3 人 31 本科: 3 人 32 33工作经历数量分布: 34 1 段经历: 2 人 35 2 段经历: 4 人 36 3 段经历: 4 人 37 38最常用技能(前10): 39 数据分析: 4 次 40 Excel: 3 次 41 机器学习: 3 次 42 SQL: 3 次 43 Python: 3 次 44 用户运营: 3 次 45 活动策划: 3 次 46 SEO/SEM: 3 次 47 Tableau: 2 次 48 统计学: 2 次 49简历数据已保存到: resumes_data.csv 50 51详细数据已保存到: resumes_data.csv 52简历分析完成! 53
核心功能代码
python-docx包
引入环境:from docx import Document
初始化文档对象:doc=Document(filepath)
Document对象就是一个Word文档对象,由一个个段落(paragraph)组成。paragraph中的属性text就是文本(字符串)
从Document对象中,也可以通过tables属性获得表格列表,表格是Table对象。表格可以通过cell(行,列)(行列数都从0开始)获取单元格,每个单元格的属性text就是文本(字符串)
csv包
初始化写入对象:
1writer = csv.DictWriter(csv文件流, fieldnames=列名列表) 2writer.writeheader() 3
写入一行:writer.writerow(dict) 传入字典参数,以列名为键,值会写入CSV
os包
- 从整个文件路径里获取文件名:
os.path.basename(filepath) - 获取文件夹下所有文件的文件名:
os.listdir(directory) - 将文件夹路径和文件名组合为文件路径:
os.path.join(directory, filename)(事实上这个函数可以叠好几层路径,可以从父文件夹叠子文件夹名再叠文件名这样叠成完整路径)
re包(正则表达式)
对正则表达式的详细介绍不在本专栏涉及的范围中。
re.search(pattern,text):搜索文本中第一个符合指定正则表达式pattern的文本,返回值的group()函数返回匹配的字符串phone_match = re.search(r'1[3-9]\d{9}', text)匹配中国大陆手机号码格式
总长度:11位数字
第一位:必须是1
第二位:必须是3-9(排除12开头的特殊号码)
后面9位:任意数字email_match = re.search(r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b', text)匹配标准邮箱格式:用户名@域名.顶级域名
用户名:字母、数字、特殊字符
域名:字母、数字、点、减号
顶级域名:至少2个字母
Python对象处理
字符串处理
strip():去除文本开头与结尾的空格、回车等控制符startswith(str):文本开头是否是特定字符串split(分隔符):将文本用分隔符切分开。如果不显式设置分隔符,默认用空格、回车等控制符来切分join(list):将字符串列表组合成一个字符串,用对象文本作为连接词isdigit():如果字符串中所有字符都是数字,返回True
容器对象处理
- 列表
- 直接通过索引切片(
[index])获取对象 append(obj):添加一个对象到列表末尾
- 直接通过索引切片(
- 字典
- 通过键值对格式可以直接创建字典对象:
1{ 2 'company': company, 3 'position': position, 4 'period': period 5}- 通过键名切片可以直接获取值和赋值(如果键名不存在,会直接创建键值对),如
resume_data['self_evaluation'] - 通过
get(key,default_value)获取值,在键(key)不存在时可以返回一个默认值(default_value)
any(obj)如果obj中任何一个元素为True,就返回True
《如何用Python处理文件:Word导出PDF & 如何用Python从Word中提取数据:以处理简历为例》 是转载文章,点击查看原文。
